Slim SEO - WPML Integration
WPML is a powerful and trusted solution for managing multilingual content in WordPress. With over 1 million active users and more than 15 years of experience, WPML has become a market leader in WordPress translation management - helping you build professional, multilingual websites with ease.
If you're using Slim SEO, you'll benefit from a seamless integration with WPML that enhances your multilingual site's SEO performance.
Translating meta titles and descriptions
Slim SEO lets you set custom meta titles and meta descriptions for each post. With WPML, you can easily translate these meta tags by following these steps:
-
Open the post you want to translate. For example, you may have a post with manually set meta title and description like this:
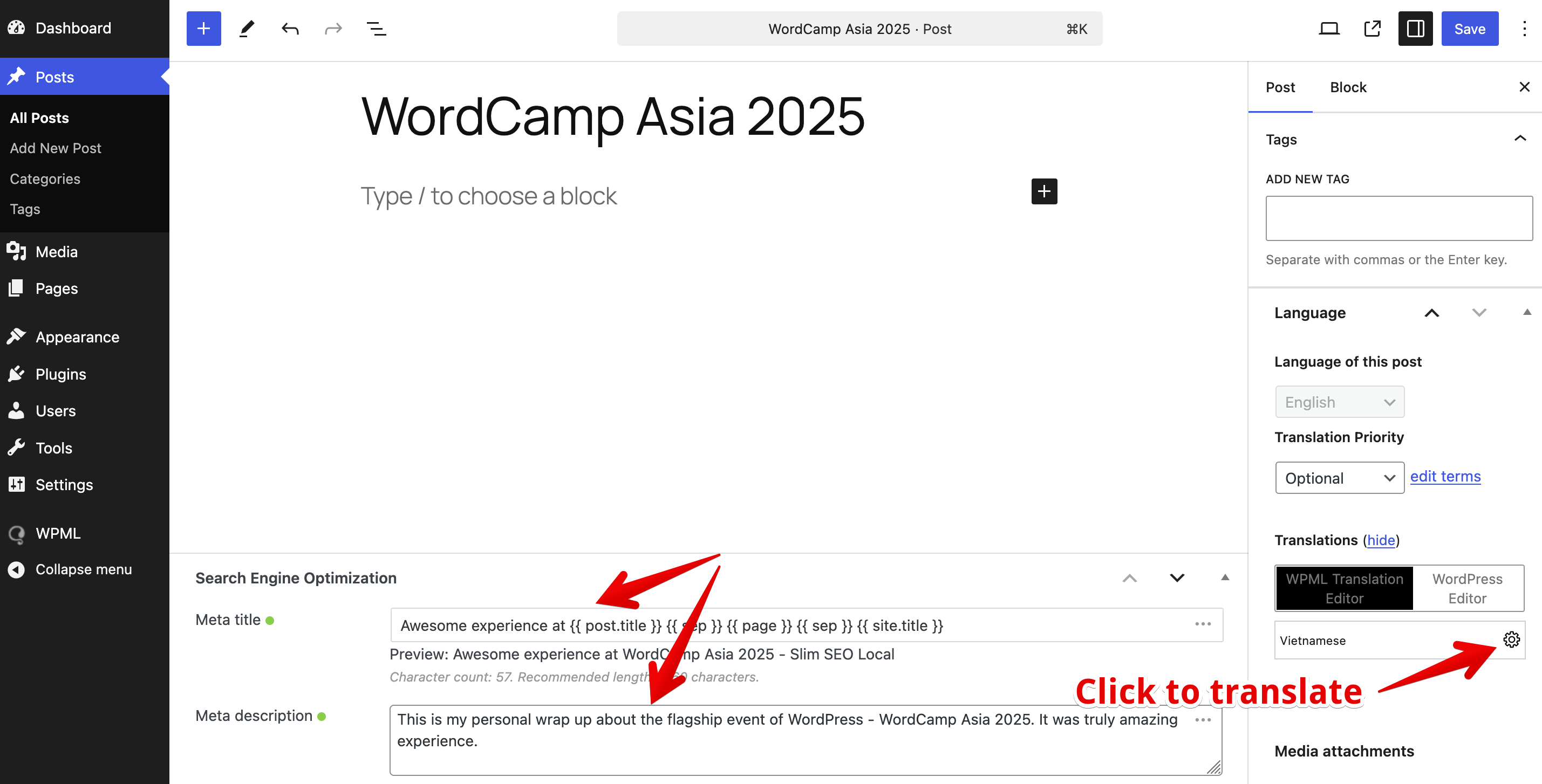
-
On the right sidebar, in the Translation section, click the plus icon (or the settings icon if the translation already exists) next to the target language.
-
WPML will open the Translation Editor where you can translate your post content - including Slim SEO's meta tags:
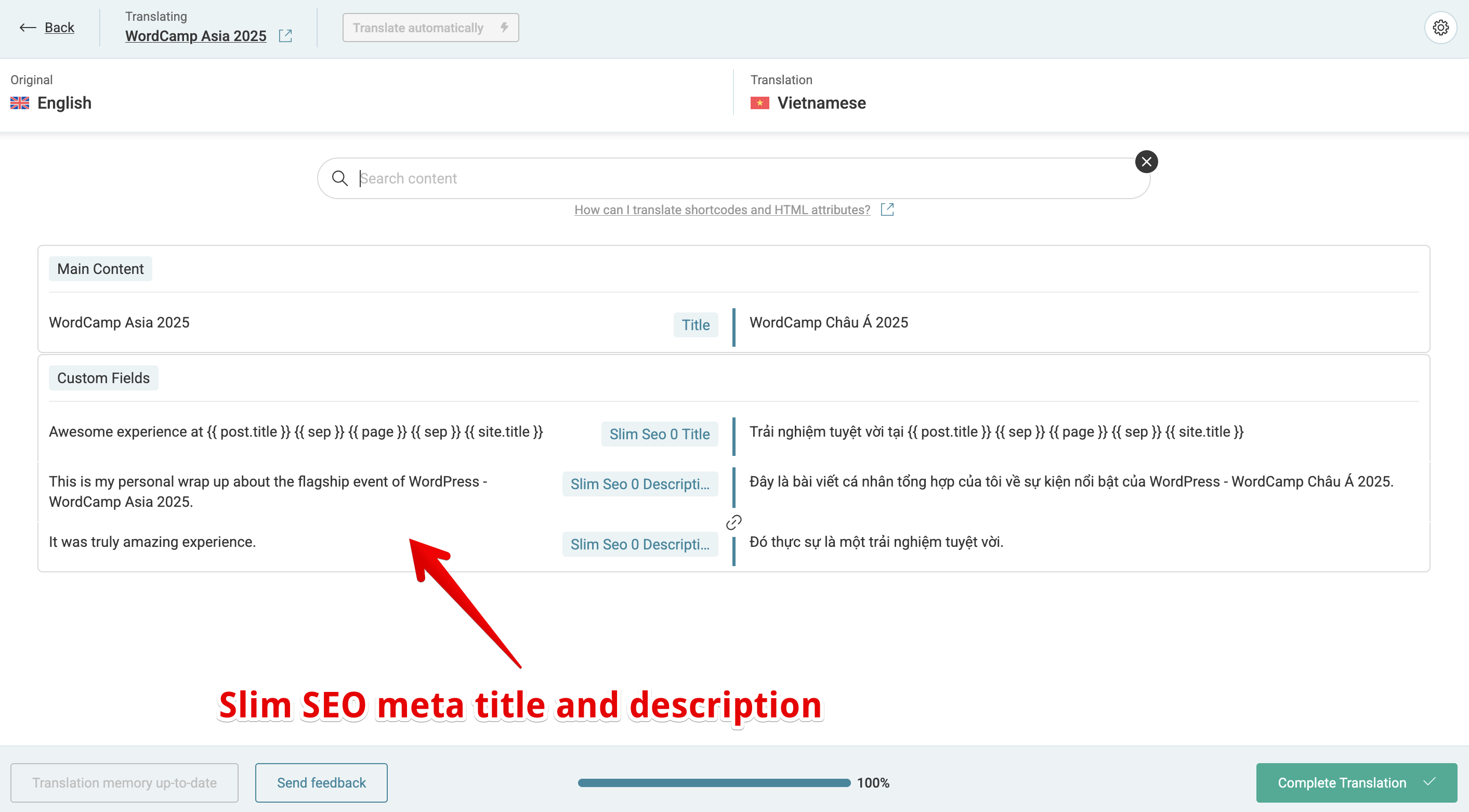
You'll see Slim SEO's meta title and description fields in the translation editor. Simply translate them as you would with other fields.
Translating meta tags settings
Slim SEO also includes a settings page where you can define default meta tags for post types and taxonomies using dynamic variables:
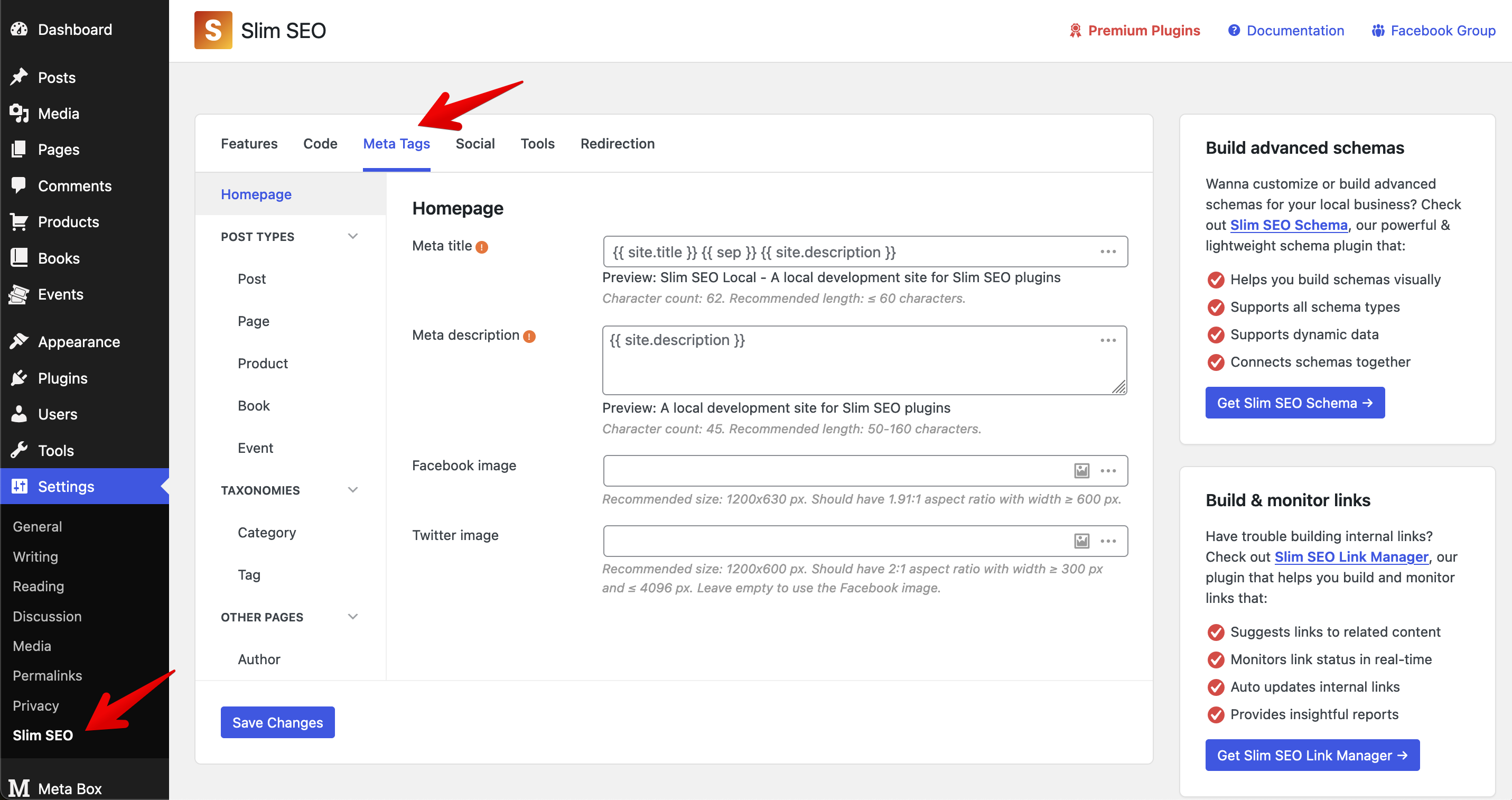
You can translate these settings using WPML's String Translation module.
To do that:
- Go to WPML → String Translation.
- Enter slim_seo in the search box to find all Slim SEO strings.
- In the results table, click the plus icon next to any setting you want to translate.
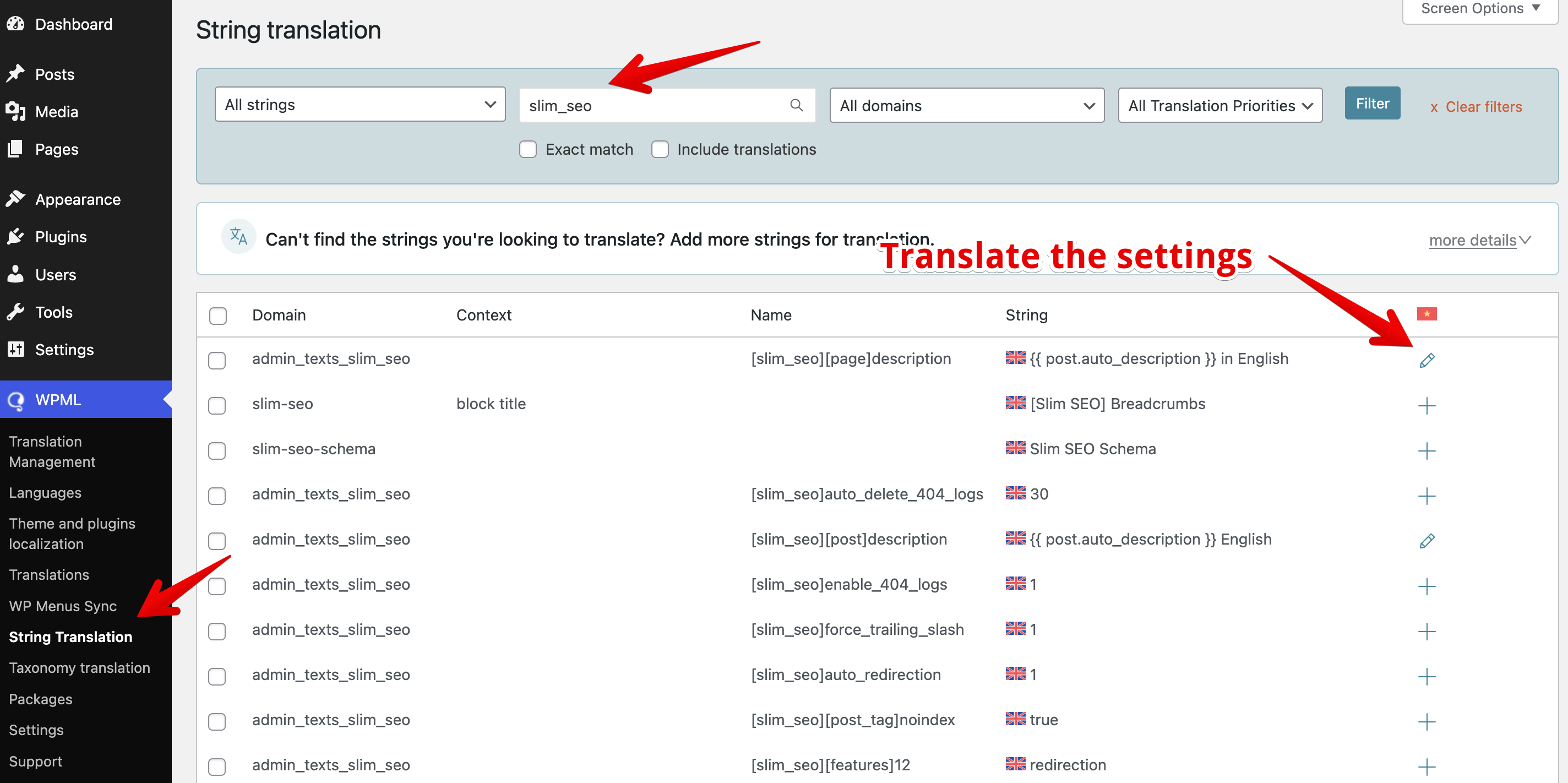
If you don't see Slim SEO settings listed, it means those settings still use their default values. To make them appear, go to Slim SEO → Meta Tags, modify the default settings, and then return to the String Translation page - the settings should now be visible.
You cannot switch languages from the admin bar and enter translations directly in the Slim SEO settings page. All translations must be done in the WPML → String Translation screen.
Hreflang tags and multilingual sitemap
Another key part of multilingual SEO is the hreflang tag. This tag helps search engines understand which version of your content to display based on a visitor's language or region.
By default, WPML automatically outputs hreflang tags in the HTML of your posts on the front end. Slim SEO doesn't need to add anything manually. Here's what that looks like:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-US" href="http://ss.test/hello-world/"/>
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="vi" href="http://ss.test/vi/hello-world/"/>
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="http://ss.test/vi/hello-world/" />
Additionally, Slim SEO automatically adds hreflang tags to your XML sitemap for each post. This helps search engines better understand your site's language structure - even though it's not visible on the front end.
Here's how it appears in the sitemap source:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<?xml-stylesheet type="text/xsl" href="http://ss.test/wp-content/plugins/slim-seo/src/Sitemaps/style.xsl"?>
<urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9"
xmlns:image="http://www.google.com/schemas/sitemap-image/1.1"
xmlns:news="http://www.google.com/schemas/sitemap-news/0.9"
xmlns:xhtml="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<url>
<loc>http://ss.test/hello-world/</loc>
<lastmod>2025-10-20T06:56:36+00:00</lastmod>
<news:news>
<news:publication>
<news:name>My Site</news:name>
<news:language>en</news:language>
</news:publication>
<news:publication_date>2025-10-20T06:56:36+00:00</news:publication_date>
<news:title>Hello world!</news:title>
</news:news>
<xhtml:link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-US" href="http://ss.test/hello-world/"/>
<xhtml:link rel="alternate" hreflang="vi" href="http://ss.test/vi/hello-world/"/>
<xhtml:link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="http://ss.test/hello-world/"/>
</url>
<url>
<loc>http://ss.test/vi/hello-world/</loc>
<lastmod>2025-10-20T06:56:36+00:00</lastmod>
<xhtml:link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-US" href="http://ss.test/hello-world/"/>
<xhtml:link rel="alternate" hreflang="vi" href="http://ss.test/vi/hello-world/"/>
<xhtml:link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="http://ss.test/hello-world/"/>
</url>
</urlset>
Both approaches - using hreflang in HTML and including them in the XML sitemap - are recommended by Google for properly handling multilingual websites.