Sitemap
Sitemap is a collection of URLs of your sites that you provide to search engines to crawl. With it, search engines know which URLs to crawl, so your website is indexed faster and no URLs are missed.
When using Slim SEO, the sitemap is automatically created at domain.com/sitemap.xml, and you need to submit this WordPress sitemap URL to search engines (in Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools).
If you don't see the sitemap when visiting the URL, please go to Settings > Permalinks and re-save the settings. Then check the sitemap URL again.
Although the sitemap is mostly used by search engines and is a technical page, Slim SEO also styles it for human reading:

To optimize the performance when generating sitemaps, the plugin splits the main sitemap into a list of smaller sitemaps:
- Post types: each post type has a sitemap.
- Taxonomies: each taxonomy has a sitemap.
The maximum number of links in a sitemap is 1000. You can use filters to change this number (see below).
Posts and terms which are manually set as "noindexed" are excluded in the sitemap.
Image sitemap
Slim SEO also includes the image sitemap by default to make sure your images are discoverable by search engines.
All the images that you insert in the post content are added to the sitemap. So, when someone searches for your images, they'll go to your posts to see the images.
The sitemap includes both self-hosted images and external images. Images in galleries or shortcodes are also parsed and included, too. For that reason, Slim SEO works with the default WordPress gallery shortcode and other WordPress gallery plugins.
Image URLs are not visible to humans when you view the sitemap link. But they're there if you view the sitemap source code as they're made for search engines only.
If you want to disable the image sitemap, use the following snippet:
add_filter( 'slim_seo_sitemap_image', '__return_false' );
Google News sitemap
Slim SEO also includes the sitemap for Google News by default to make sure your posts can be submitted to Google News.
The news sitemap is enabled for the default post type post only. It's not available for other post types. Slim SEO automatically adds details for news in the sitemap-post-type-post.xml sitemap (the sitemap for post). So you can use this URL https://domain.com/sitemap-post-type-post.xml to submit news sitemap to Google (or you can simply submit https://domain.com/sitemap.xml as usual as Google will discover the news sitemap by going through each sub-sitemap).
Similarly to the image sitemap, the details for news sitemap are not visible to humans when you view the sitemap link. But they're there if you view the sitemap source code as they're made for search engines only.
If you want to disable the news sitemap, use the following snippet:
add_filter( 'slim_seo_sitemap_news', '__return_false' );
Sitemap and robots.txt
The sitemap URL is automatically included in the robots.txt on your website if your website doesn't have a physical robots.txt file. WordPress automatically creates a virtual robots.txt for your website at domain.com/robots.txt. If you have a physical robots.txt, you need to add the sitemap URL by yourself.
Multilingual sitemap
Slim SEO integrates well with multilingual plugins like WPML, Polylang, and TranslatePress.
Slim SEO strictly follows Google's guidelines on creating a multilingual sitemap. According to the guidelines, the plugin adds rel="alternate" for every alternate version of the post or term in the sitemap. When the search engines view the sitemap, they see multiple links for all languages for each post. These links are not visible to humans, but you can see them when viewing the sitemap source code.
By following this method from Google, you won't have separated sitemaps for different languages. Instead, you'll have a global sitemap at example.com/sitemap.xml for all languages.
For more details about multilingual sitemap, please see this article: How to create a multilingual sitemap in WordPress.
Excluding post types
To exclude a post type from the sitemap, please go to Settings > Slim SEO and select the Meta Tags tab. Then pick a post type and enable the option Hide from search engines:
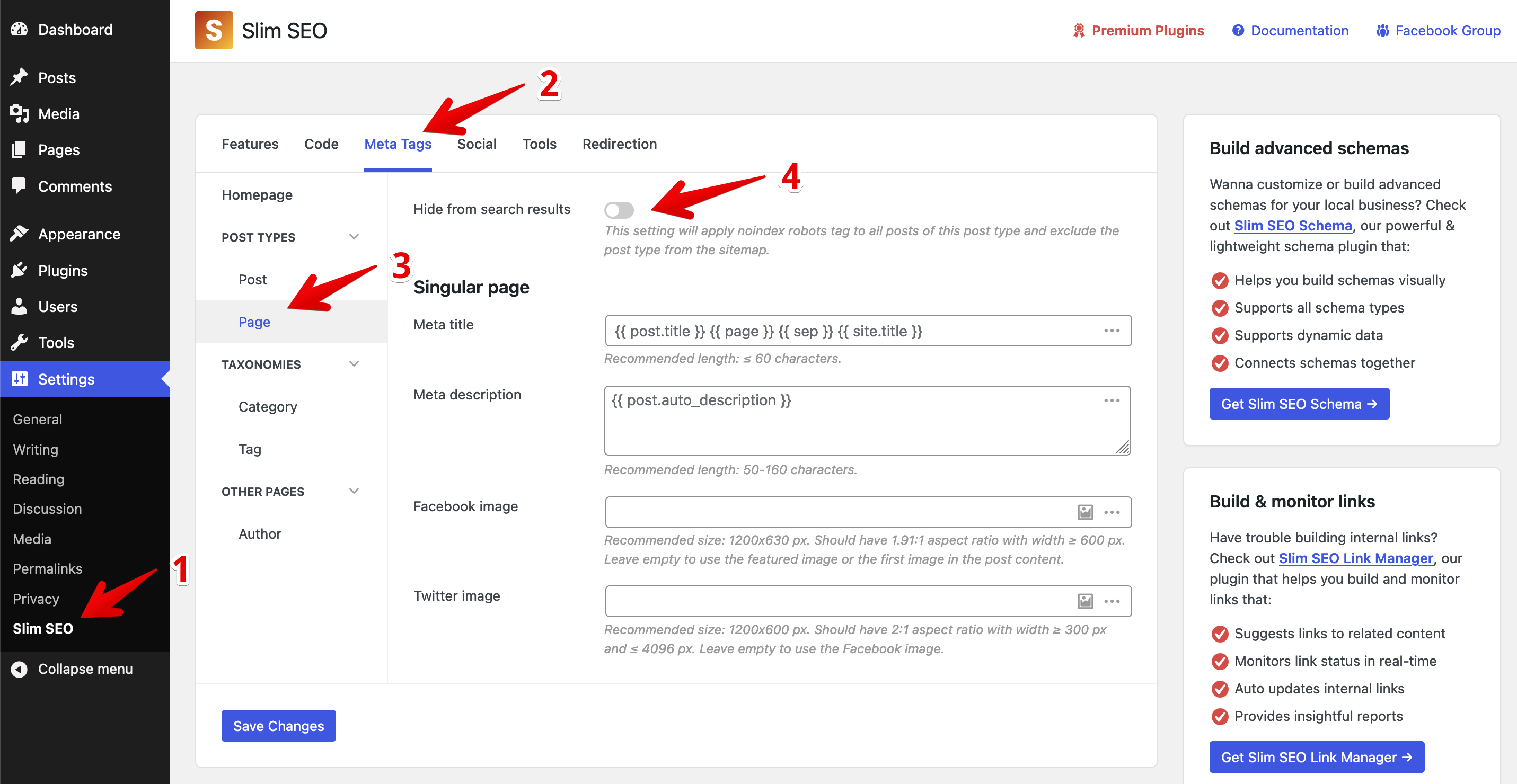
You can also use the following snippet:
add_filter( 'slim_seo_sitemap_post_types', function( $post_types ) {
return array_diff( $post_types, ['post_type_1', 'post_type_2'] );
} );
Excluding post types does not tell search engines to not index them. It simply doesn't send the post types' URLs to search engines. If search engines can discover posts in another way (by crawling your site), then they still can index them.
To tell search engines to not index these posts, it's better to use the robots tag.
Excluding taxonomies
Similar to the above, if you want to exclude a taxonomy from the sitemap, please go to Settings > Slim SEO and select the Meta Tags tab. Then pick a taxonomy and enable the option Hide from search engines.
You can also use the following snippet:
add_filter( 'slim_seo_sitemap_taxonomies', function( $taxonomies ) {
return array_diff( $taxonomies, ['tax_1', 'tax_2'] );
} );
If you want to remove all taxonomies from the sitemap, use the following code:
add_filter( 'slim_seo_sitemap_taxonomies', '__return_empty_array' );
Post query
To get posts for the sitemap, Slim SEO makes a query to the database. If you want to change the query (for example, changing the number of posts per page or excluding some posts), then use the following snippet:
add_filter( 'slim_seo_sitemap_post_type_query_args', function( $query_args ) {
// Change the number of URLs
$query_args['posts_per_page'] = 5000;
return $query_args;
} );
The parameters are the same as in the WP_Query class.
Taxonomy query
Similar to the above, if you want to change the query to get taxonomy terms, please use this snippet:
add_filter( 'slim_seo_taxonomy_query_args', function( $query_args ) {
// Change the number of URLs
$query_args['number'] = 5000;
return $query_args;
} );
The query parameters are the same as in the get_terms() function.
User sitemap
By default, Slim SEO doesn't include the user sitemap. If you want to enable user sitemap, please use the following snippet:
add_filter( 'slim_seo_user_sitemap', '__return_true' );
If you want to include only some users in the sitemap, you can change the user query args like this:
add_filter( 'slim_seo_user_query_args', function( $args ) {
$args['role'] = 'administrator';
return $args;
} );
The parameters are the same as in the get_users() function.
Adding more URLs to the post sitemap
Slim SEO has a hook slim_seo_sitemap_post that allows you to add more URLs to each post entry in the sitemap. It's good if you want to add more URLs like image URLs or language URLs to each post in the sitemap.
add_action( 'slim_seo_sitemap_post', function( WP_Post $post ) {
// Add image URL from a custom field.
$custom_image_url = get_post_meta( $post->ID, 'custom_image_url', true );
if ( ! $custom_image_url ) {
return;
}
echo "\t\t<image:image>\n";
echo "\t\t\t<image:loc>", esc_url( $custom_image_url ), "</image:loc>\n";
echo "\t\t</image:image>\n";
} );
If you want to add URLs (like other posts) to the sitemap, you can use output them like this:
add_action( 'slim_seo_sitemap_post', 'ss_add_custom_posts_to_sitemap' );
function ss_add_custom_posts_to_sitemap() {
// Used to make sure we output only once.
static $output = false;
if ( $output ) {
return;
}
// Close the current `<url>` entry.
echo "\t</url>\n";
// List of custom URLs you want to add to the sitemap.
$urls = [
'https://domain.com/page-1',
'https://domain.com/page-2',
];
foreach ( $urls as $i => $url ) {
echo "\t<url>\n";
echo "\t\t<loc>", esc_url( $url ), "</loc>\n";
// Do not output the closing tag for the last URL.
if ( $i < count( $urls ) - 1) {
echo "\t</url>\n";
}
}
// Don't output next time.
$output = true;
}
Core sitemaps
Since version 5.5, WordPress includes sitemap functionality in the core. However, the core sitemaps lack some features that Slim SEO provides:
- Image sitemap: Slim SEO's sitemap includes images, which makes your site appear when people search for images.
- Google News sitemap: Slim SEO supports Google News sitemap, which makes your articles appear on Google News.
- Multilingual sitemap: each entry in the sitemap has its versions in other languages, which lets search engines know to index multilingual URLs, and your site might appear when people search in another language.
Because of these reasons, we disable the core sitemaps to avoid any conflict.